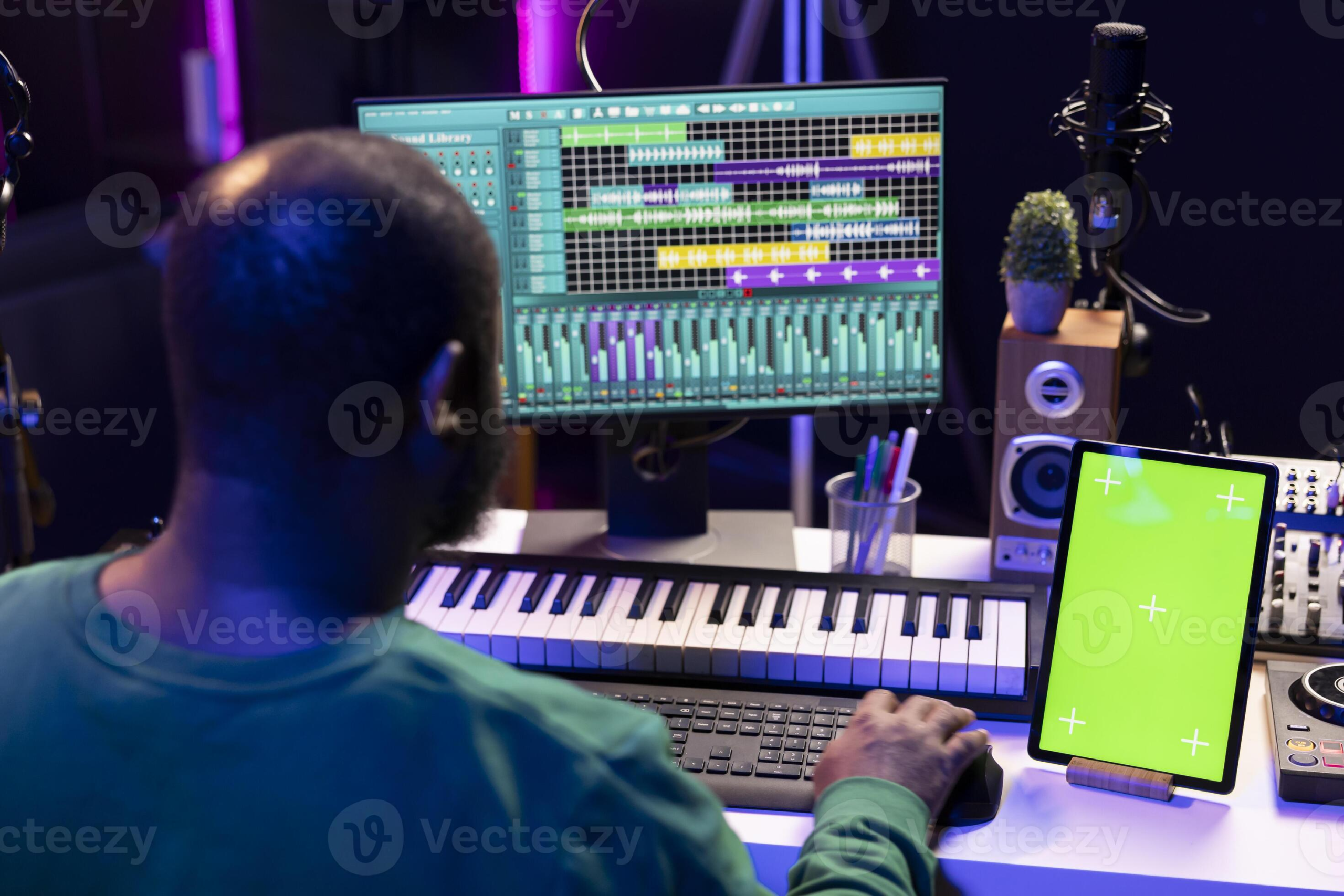
The podcasting landscape has exploded in recent years, with millions of shows competing for listener attention. What once required expensive studio equipment and technical expertise can now be accomplished with a laptop and basic accessories. However, this accessibility creates a new challenge: standing out in an increasingly crowded medium. Mastering podcast production techniques has become essential for creators who want their shows to achieve professional quality and attract dedicated audiences.
The Podcast Production Journey: An Overview
Successful podcast production involves a comprehensive workflow that extends well beyond simply recording and uploading audio. Understanding each phase of this journey provides the foundation for creating truly professional content.
Pre-Production: Laying the Groundwork
Before you press record, thoughtful preparation establishes the foundation for everything that follows:
- Concept Development: Defining your podcast’s purpose, target audience, and unique value proposition
- Format Selection: Choosing the structure that best serves your content (interview, narrative, roundtable, etc.)
- Episode Planning: Creating outlines, research documents, and question lists
- Scheduling: Coordinating with guests, co-hosts, and production team members
- Technical Setup: Preparing your recording environment and equipment
Effective pre-production minimizes unexpected challenges during recording and establishes a consistent framework for your show’s identity.
Production: Capturing Quality Audio
The recording phase focuses on creating the cleanest, most engaging raw materials possible:
- Recording Environment: Optimizing acoustics and minimizing background noise
- Microphone Technique: Proper positioning and speaking practices
- Performance Direction: Guiding hosts and guests to deliver natural, engaging content
- Technical Monitoring: Watching levels and addressing issues in real-time
- Backup Systems: Creating redundancies to prevent catastrophic losses
The quality of your raw recording significantly impacts every subsequent production step, making this phase particularly crucial.
Post-Production: Crafting the Final Product
This transformation phase turns raw recordings into polished, broadcast-ready episodes:
- Editing: Removing errors, tightening pacing, and enhancing narrative flow
- Sound Design: Adding music, sound effects, and atmospheric elements
- Mixing: Balancing audio elements for clarity and engagement
- Mastering: Optimizing final audio for consistent volume and quality across platforms
- Metadata Preparation: Creating episode titles, descriptions, and show notes
Post-production is where your podcast truly develops its professional identity and listener-friendly qualities.

Essential Audio Recording Fundamentals
Understanding basic audio recording basics creates the foundation for professional podcast production.
Creating an Optimal Recording Environment
Your recording space significantly impacts audio quality:
- Acoustic Treatment: Use soft materials (blankets, foam panels, rugs) to reduce reflections and echo
- Background Noise Reduction: Turn off HVAC, refrigerators, and other noise sources during recording
- Isolation Techniques: Record in closets or under blankets when professional spaces aren’t available
- Consistency: Use the same recording environment for all episodes when possible
Even modest improvements to your recording space can dramatically enhance audio quality.
Microphone Selection and Technique
Microphone choices and usage practices directly affect your sound:
- Microphone Types: Dynamic microphones (like the Shure SM58) excel in untreated spaces, while condenser microphones offer greater detail in controlled environments
- Polar Patterns: Cardioid patterns reduce side and rear noise, while omnidirectional captures room ambiance
- Positioning: Maintain consistent distance (typically 4-6 inches) and angle from the microphone
- Pop Filters: Use screens to reduce plosives (“p” and “b” sounds that create bursts of air)
- Stands and Boom Arms: Provide stable positioning and isolate handling noise
Understanding these fundamentals helps you make informed equipment decisions based on your specific needs and environment.
Digital Recording Fundamentals
Optimal technical settings ensure clean digital captures:
- Sample Rate: 44.1kHz is standard for podcasts (matching CD quality)
- Bit Depth: 16-bit provides sufficient dynamic range for voice recording
- Recording Levels: Target peaks between -12dB and -6dB to prevent distortion while maintaining good signal-to-noise ratio
- File Formats: Record in uncompressed WAV or AIFF formats for editing, saving compressed MP3 for distribution only
These technical considerations may seem minor, but they establish the foundation for professional sound quality.
Advanced Recording Techniques
Beyond fundamentals, several advanced techniques can elevate your podcast’s production quality.
Remote Recording Solutions
For interviews with distant guests:
- Double-Ender Recording: Both host and guest record their audio locally, then files are synchronized in post-production
- Remote Recording Platforms: Services like Squadcast, Zencastr, and Riverside.fm record separate high-quality tracks for each participant
- Backup Recording: Always record a backup via Zoom or similar platforms in case primary recording fails
- Pre-Interview Technical Checks: Test connections, levels, and recording systems before beginning content recording
These approaches help overcome the quality limitations inherent in standard video conferencing platforms.
Multi-Microphone Setups
For in-person group recordings:
- Microphone Isolation: Position microphones to minimize bleed between speakers
- Interface Selection: Choose audio interfaces with sufficient preamps for your microphone count
- Monitoring Solutions: Use headphones for all participants to prevent speaker feedback
- Level Balancing: Adjust individual input gains to accommodate different speaking volumes
- Track Organization: Label and organize multi-track recordings to streamline editing
Properly executed multi-microphone recording creates a natural conversational feel while maintaining editing flexibility.
Field Recording Considerations
For on-location podcast segments:
- Portable Recorders: Select recorders with good preamps and built-in limiters
- Wind Protection: Use windscreens and “dead cat” covers for outdoor recording
- Ambient Capture: Record room tone and environmental sound for natural transitions
- Monitoring: Always monitor through headphones to catch problems immediately
- Battery Management: Carry spares and check power levels frequently
Environmental recording adds texture and authenticity to documentary-style podcasts.

Mastering Podcast Editing Techniques
Editing transforms raw recordings into engaging, professional content that respects listeners’ time and attention.
Structural Editing Approaches
These techniques focus on content and pacing:
- Content Mapping: Organize content thematically rather than strictly chronologically
- Intro/Outro Development: Create consistent openings and closings that establish show identity
- Segment Transitions: Design smooth movements between topics using music or verbal bridges
- Narrative Enhancement: Restructure conversations to improve storytelling flow
- Pacing Adjustment: Tighten extended discussions while preserving natural conversation rhythms
Effective structural editing creates a compelling listener journey while maintaining authenticity.
Technical Editing Skills
These operations focus on audio quality improvement:
- Removal of Mistakes: Edit out verbal stumbles, false starts, and technical issues
- Breath Editing: Reduce or remove distracting breath sounds while maintaining natural speech patterns
- Silence Optimization: Adjust pause lengths for improved pacing
- Crosstalk Management: Clean up overlapping conversations for clarity
- Consistency Creation: Normalize energy levels and speaking styles across sections recorded separately
These techniques create professional polish while preserving the natural qualities that make podcasts engaging.
Dialogue Enhancement Tools
Software tools can further refine voice recordings:
- Noise Reduction: Remove consistent background sounds like computer fans or air conditioning
- De-essing: Reduce harsh sibilance (“s” sounds) that can be grating at high volumes
- EQ Adjustment: Enhance voice clarity through frequency balancing
- Compression: Control volume variations for consistent listening experience
- Restoration Tools: Address specific audio problems like clicks, pops, and room resonance
While these tools are powerful, subtle application preserves natural vocal qualities.
Creative Sound Design for Podcasts
Beyond clean dialogue, thoughtful sound design adds dimension and identity to your podcast.
Music Selection and Integration
Music establishes emotional tone and reinforces your brand:
- Theme Development: Create consistent opening and closing themes that become associated with your show
- Segment Indicators: Use musical motifs to signal transitions between show segments
- Emotional Underlays: Support emotional content with subtle musical beds
- Licensing Considerations: Properly license all music through royalty-free services, direct composer relationships, or public domain sources
- Mix Balance: Ensure music enhances rather than competes with dialogue
Thoughtful music integration creates a signature sound that distinguishes your show from competitors.
Sound Effects and Ambient Audio
Additional audio elements create texture and immersion:
- Environmental Sounds: Establish setting through location-specific ambience
- Transitional Effects: Use sound design elements for scene changes
- Illustrative Effects: Reinforce concepts mentioned in dialogue
- Sonic Branding: Develop signature sound effects for recurring segments
- Layering Techniques: Build rich soundscapes through multiple complementary elements
These elements transform podcasts from simple conversations into immersive audio experiences.
Voice Processing for Character and Clarity
Voice treatment helps establish identity and improves listening experience:
- EQ Profiles: Develop consistent equalization settings for regular hosts
- Compression Strategies: Apply appropriate dynamics processing for different voices
- Character Enhancement: Subtly emphasize vocal qualities that define your hosting personality
- Clarity Processing: Apply targeted treatment to improve intelligibility
- Consistent Leveling: Ensure volume remains consistent across episodes and segments
These techniques create a signature sound while ensuring comfortable listening across different environments.
Mixing and Mastering for Podcast Distribution
The final technical stages prepare your podcast for optimal listening across platforms and devices.
Professional Mixing Techniques
Mixing balances all audio elements:
- Level Balancing: Set appropriate volume relationships between voices, music, and effects
- Panning Decisions: Create spatial relationships through stereo positioning
- Frequency Management: Ensure different elements occupy distinct frequency ranges
- Automation: Adjust levels dynamically throughout the episode as needed
- Perspective Creation: Establish consistent audio “staging” that feels natural
Effective mixing creates a cohesive sonic experience that guides listener attention appropriately.
Mastering for Podcast Platforms
Final processing prepares your audio for distribution:
- Loudness Standardization: Target appropriate loudness levels (-16 to -18 LUFS for podcasts)
- Dynamic Range Management: Ensure comfortable listening in various environments
- Format Optimization: Export in appropriate formats for distribution platforms
- Metadata Integration: Embed episode information and artwork
- Quality Control: Perform final checks across different playback systems
Proper mastering ensures your podcast sounds professional across different listening platforms and environments.
Podcast Editing Software Selection
Choosing the right tools for your workflow:
- Digital Audio Workstations: Professional options include Adobe Audition, Logic Pro, and Pro Tools
- Podcast-Specific Editors: Specialized tools like Hindenburg Journalist and Descript
- Free Alternatives: Options like Audacity for those with limited budgets
- Remote Collaboration Tools: Platforms that support team editing workflows
- Plugin Consideration: Additional processing tools that extend your software’s capabilities
The ideal software combines sufficient capabilities with an interface that matches your technical comfort level.
Distribution and Publishing Best Practices
Creating your podcast is only part of the journey—effective distribution ensures it reaches your intended audience.
Hosting Platform Selection
Your hosting provider serves as your podcast’s technical foundation:
- Storage and Bandwidth: Sufficient resources for your publishing schedule and audience size
- Analytics Capabilities: Detailed metrics to understand audience behavior
- RSS Management: Reliable feed creation and maintenance
- Monetization Options: Features that support your business model
- Distribution Network: Automated publishing to major podcast directories
Choose providers that offer the specific features most important to your podcast’s goals and growth strategy.
Metadata Optimization
Proper metadata improves discoverability:
- Episode Titles: Clear, descriptive, and engaging titles that include relevant keywords
- Show Notes: Comprehensive descriptions with timestamps, links, and key points
- Categorization: Appropriate primary and secondary category selection
- Keyword Integration: Natural inclusion of search terms relevant to your content
- Artwork Optimization: High-quality, distinctive images that represent your brand
These elements help potential listeners find and evaluate your podcast across distribution platforms.
Promotion and Audience Growth
Distribution extends beyond technical publishing:
- Cross-Platform Strategy: Sharing content across social media, newsletters, and websites
- Audiogram Creation: Converting key moments into shareable video clips
- Transcription Benefits: Providing text versions for accessibility and SEO advantages
- Release Scheduling: Maintaining consistent publication timing
- Community Engagement: Fostering audience interaction and participation
The most successful podcasts combine production excellence with strategic promotion.
Conclusion
Mastering podcast production techniques represents a journey of continuous improvement rather than a fixed destination. As you develop your skills across pre-production, recording, editing, and distribution, your podcast will evolve from amateur experiment to professional media property.
The most successful podcasters balance technical excellence with authentic content, recognizing that production quality supports rather than replaces compelling subject matter. By implementing the techniques outlined in this guide, you’ll create a professional foundation that allows your unique voice and perspective to reach listeners with maximum impact.
Whether you’re creating an independent passion project or developing branded content for an organization, these production principles will help your podcast stand out in an increasingly competitive audio landscape. The combination of thoughtful preparation, quality recording, skillful editing, and strategic distribution creates podcasts that not only attract listeners but keep them coming back episode after episode.
Recommended Resources
For those looking to further develop their podcast production skills:
- Equipment review websites that provide honest assessments of recording gear
- Online courses focused on specific aspects of audio production
- Podcast production communities where creators share techniques and solutions
- Industry events that provide hands-on learning opportunities
- Technical forums for troubleshooting specific audio challenges

